The Leading Cause of Death Worldwide
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. CVD is responsible for an estimated 18 million deaths each year, and approximately 1 in every 3 people dies of CVD globally. Myocardial infarction, commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow to the heart is blocked, leading to tissue damage. Restoring blood flow is essential, but it can also result in further harm due to inflammation, oxidative stress, and cell death. This damage significantly increases the risk of developing heart failure, a condition impacting over 64 million people globally. Addressing myocardial infarction's aftermath is critical to reducing heart failure rates and improving patient outcomes.
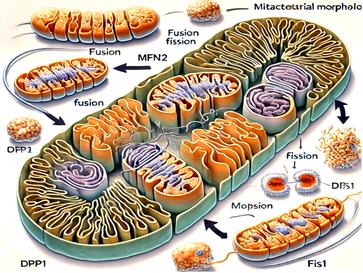
The Powerhouse of the Cell
Mitochondria are responsible for the production of most of the adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and they play central roles in maintaining cellular metabolic homeostasis, cell survival and cell death. The heart consumes about 6-30 kg of ATP per day, emphasizing the importance of mitochondrial homeostasis for normal cardiomyocyte function. In the context of myocardial infarction, disrupted mitochondrial dynamics play a significant role in cardiac injury. Excessive mitochondrial fission and impaired fusion during myocardial infarction contribute to energy deficits, increased oxidative stress, and cell death. Understanding mitochondrial dynamics in this setting offers valuable insights into potential therapeutic targets to protect the heart and improve recovery after ischemic injury.
A Promising Approach in Medicine
Peptide therapeutics offer high specificity, low toxicity, and the ability to target protein-protein interactions that are often inaccessible to small molecules or biologics. In the context of mitochondrial dynamics during myocardial infarction, peptides can be designed to modulate key processes like fusion and fission, reducing oxidative stress and preserving mitochondrial function. This targeted approach holds great promise for minimizing cardiac damage and improving recovery after ischemic injury.
Our Mission and Goals
At Qvit Lab, our goal is to bridge the gap between fundamental research and clinical applications by developing innovative peptide-based therapies for cardiovascular diseases. We aim to uncover the intricate roles of mitochondrial proteins and their regulation through peptides to address key challenges in myocardial infarction and heart failure. By integrating computational design, peptide synthesis, and advanced testing in cellular and animal models, we strive to translate our findings into impactful treatments that improve patient outcomes and advance the field of cardiovascular medicine